With the aid of concentrated abrasive grains contained in a nozzle, abrasive jet machining removes material by impact erosion. A high-velocity jet containing abrasive particles is directed onto the workpiece surface under regulated circumstances during abrasive-jet machining. The material is removed by eroding the work material with abrasive grits at a speed of 150-300m/s, creating a sufficiently concentrated force to accomplish operations like cutting. Read More…
MetPlas is your single source for cutting edge contract manufacturing. This ISO 9001-2008 registered manufacturer offers expertise in lean manufacturing & a wide range of precision machining, waterjet cutting & assembly of metals & plastics. OEM’s have relied on MetPlas for decades to meet their quality, schedule & budget needs. The logical choice for virtually any contract manufacturing...

Since 1988, MET Manufacturing Group, LLC has been a trusted provider of quality waterjet cutting services. Our water jet equipment is great for prototyping, fast and reliable for production, and can quickly change from job to job. Material cutting capabilities include plastic, rubber, copper, aluminum, titanium, and many more. Tolerances for certain applications can be held at +- .001". Contact...

As a full-service waterjet machining center, RTD Manufacturing uses waterjet cutting in the manufacture of our products. Besides waterjet cutting, we also use EDM wire cutting; detail and manual machining; CNC machining plus production drill and tap. We have prototype manufacturing to offer as well.
Arcadia operates one of the largest waterjet job shops in the eastern U.S., manufacturing custom-cut parts and shapes for a variety of industries. We provide waterjet cutting services using large capacities and 5-axis water jet machining. Allow our experience to improve your manufacturing process.

We provide top of the line water jet cutting here at West Coast Waterjet. We are ISO 9001:2008 certified and our experts have a wide experience of waterjet cutting for a wide variety of industries. Our services are for virtually any material and we will work with you every step of the way. Please give us a call today to learn more information!

More Abrasive Jet Machining Companies
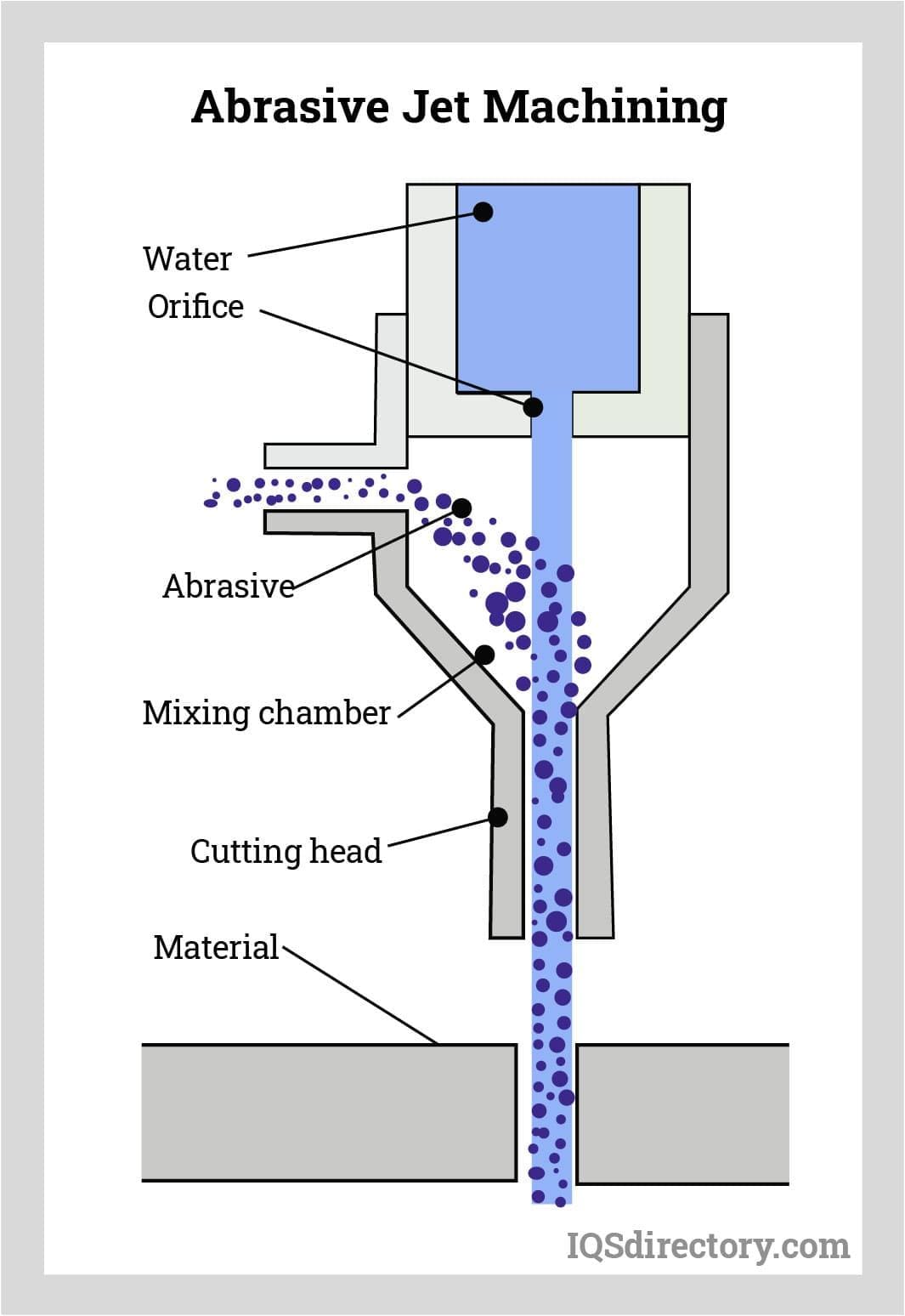
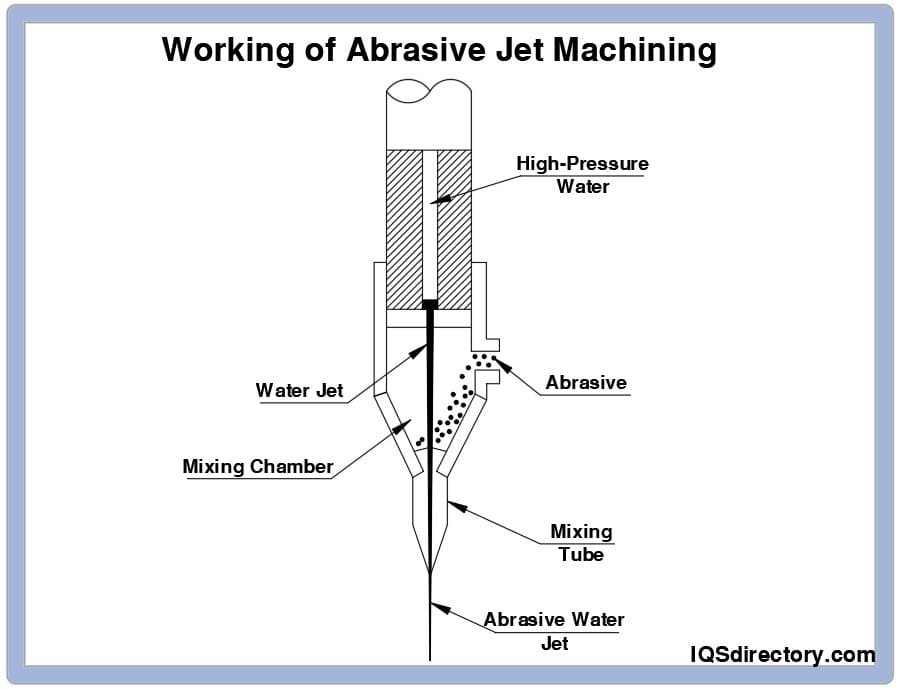
How Abrasive Jet Machining Works
An air compressor-connected special machine is used for abrasive jet machining. Inert air or gas can be used in the air compressor. A nozzle directs fine particulate matter during the process in the direction of the workpiece. Abrasive jet machining employs extremely small particles, frequently with a diameter of under 0.001 inches.
As the abrasive particles and gas mixture touches the workpiece, material is removed from its surface. The majority of abrasive jet devices are bench-mounted. Therefore, a compressor can mix the gas and the abrasive particles while positioned on a bench. In front of the machine, the workpiece is then placed. Next, the machine is turned on, and the nozzle is placed where the material needs to be removed from the workpiece.
Parts of Abrasive Jet Machines
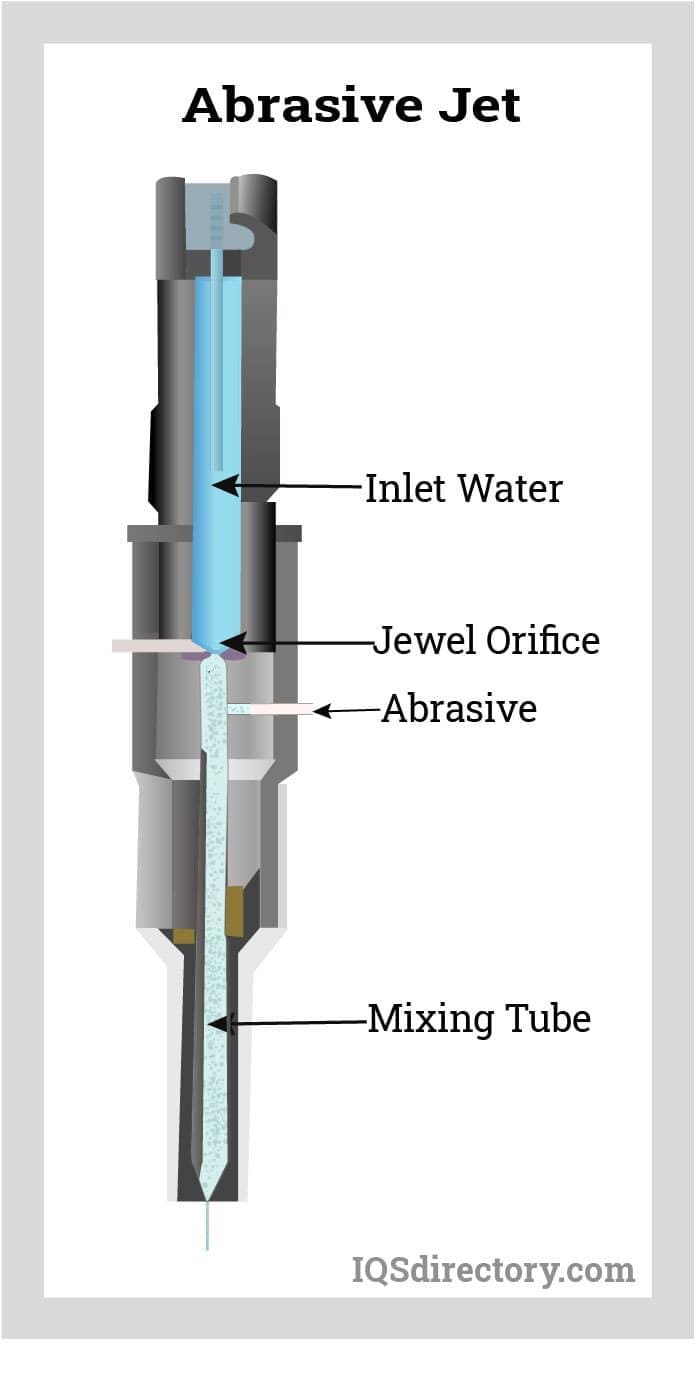
High Pressure Water/Gas Supply Chamber
An abrasive jet machine starts its process by being fed a source of high-pressure water or gas. Nitrogen, carbon dioxide, or fresh air are the gasses used. The filtered gas is subsequently fed into a connecting hose where it is delivered to the mixing chamber containing the abrasive powder at a pressure of 2 to 8 kg/cm and vibrating at 50 Hz.
Abrasive
Simultaneously, the chosen abrasive material is fed into the machine through a separate opening. The most common abrasives used are silicon carbide, aluminum oxide, glass powder, or sodium bicarbonate that has been properly produced. The range of typical particle sizes is from 10 to 50 microns. For precise work and fine surface polish, smaller sizes are required. Larger sizes are employed for quick clearance rates.
Dolomite (calcium magnesium carbonate) at a 200 grit size is also effective for light cleaning and etching, in addition to the abrasives mentioned above. For gentle polishing and deburring, glass beads with a diameter of 0.30 to 0.60 mm are employed.
Mixing Chamber
The high pressure water (or gas) and abrasive meet and are mixed together in the mixing chamber. The mixing chamber's vibrational amplitude regulates the rate at which abrasive powder is fed. A pressure regulator regulates the flow and pressure of the gas. Cams, pantographs, or other suitable devices are used to move the workpiece to the nozzle to adjust the size and shape of the cut.
Nozzle/Mixing Tube
Finally, this gas (or water) and abrasive mixture is released from a tiny nozzle fixed to a fixture at a speed of 150 to 300 m/min. Nozzles are built of strong materials like tungsten carbide or synthetic sapphire because they have a high rate of abrasion wear. The typical lifespan of tungsten carbide nozzles is 8 to 12 hours. While sapphire nozzles, when used with 27-micron abrasive powder, operate for almost 300 hours
Workrate/Efficiency
The diameter of the nozzle, the abrasive gas mixture's composition, the hardness of the work material and the abrasive particles, the size of the particles, the jet's velocity, and the separation between the workpiece and the jet all affect how much metal is removed from the surface. As a result, abrasive jet machining creates a slower material removal rate when compared to other material removal processes. However, the process is highly effective and accurate, leading to its use as a finishing procedure.
Applications of Abrasive Jet Machining
- It is more cost-effective than etching or grinding and is used for rubbing and frosting glass, ceramics, and refractories.
- Metal layering that has been cleaned, such as a resistive coating
- Cutting the separating lines of injection-molded components and forgings, as well as deflashing tiny castings
- Registration numbers are engraved on toughened glass used for car windows.
- For cutting thin, delicate materials like germanium, silicon, quartz, mica, etc., AJM is employed.
- Abrasive jet machining is used to effectively fabricate micro modules.
- Deburring brittle and hard materials involves drilling, etching, cutting, and polishing.
- Brittle materials can be micro-machined using it.
- It is used to clean metallic cavities and molds.
- Removing rust, paints, glues, and other impurities from surfaces
- Deburring of nylon, Teflon™, Delrin®, hydraulic valves, and surgical needles
- Employed to engrave glass
Advantages of Abrasive Jet Machining
- One can achieve a high level of surface polish.
- Any harm is not severe.
- For cutting glass and ceramics, it delivers a cool cutting action, enabling the machining of delicate, heat-sensitive materials.
- There is no contact between the workpiece and the tool, so there is no chatter or vibration during the process.
- Abrasive jet machining has a minimal capital cost since it is simple to use.
- Like germanium, hard materials with thin sections can be machined.
Disadvantages of Abrasive Jet Machining
- A low material removal rate causes the process' capacity to be lower.
- Abrasive embeds itself during the machining of soft materials, reducing the surface finish.
- The tapering of the hole brought on by the inevitable variation of an abrasive jet disturbs the cutting accuracy.
- Inaccuracy is a problem leading to stray cutting.
- An additional expense will be necessary since a dust collecting system is a fundamental requirement to stop atmospheric pollution and health risks.
- Nozzle life is constrained (300 hours).
- Because the sharp edges of abrasive powders are worn out, and smaller particles can jam the nozzle, they cannot be used again.
- A short standoff distance can harm the nozzle
- Due to the abrasive jet's flaring effect, the process’ precision could be better.
- There will be a taper in deep holes.
- The abrasive jet machining process pollutes and creates damage to the environment.
- Airborne abrasives can create a dangerous work environment.
Choosing the Correct Abrasive Jet Machining Company
To make sure you have the most positive outcome when selecting an abrasive jet machining company, it is important to compare at least 4 companies using our abrasive jet machining directory. Each abrasive jet machining company has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the company for more information or request a quote. Review each abrasive jet machining company website using our proprietary website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple abrasive jet machining companies with the same form.








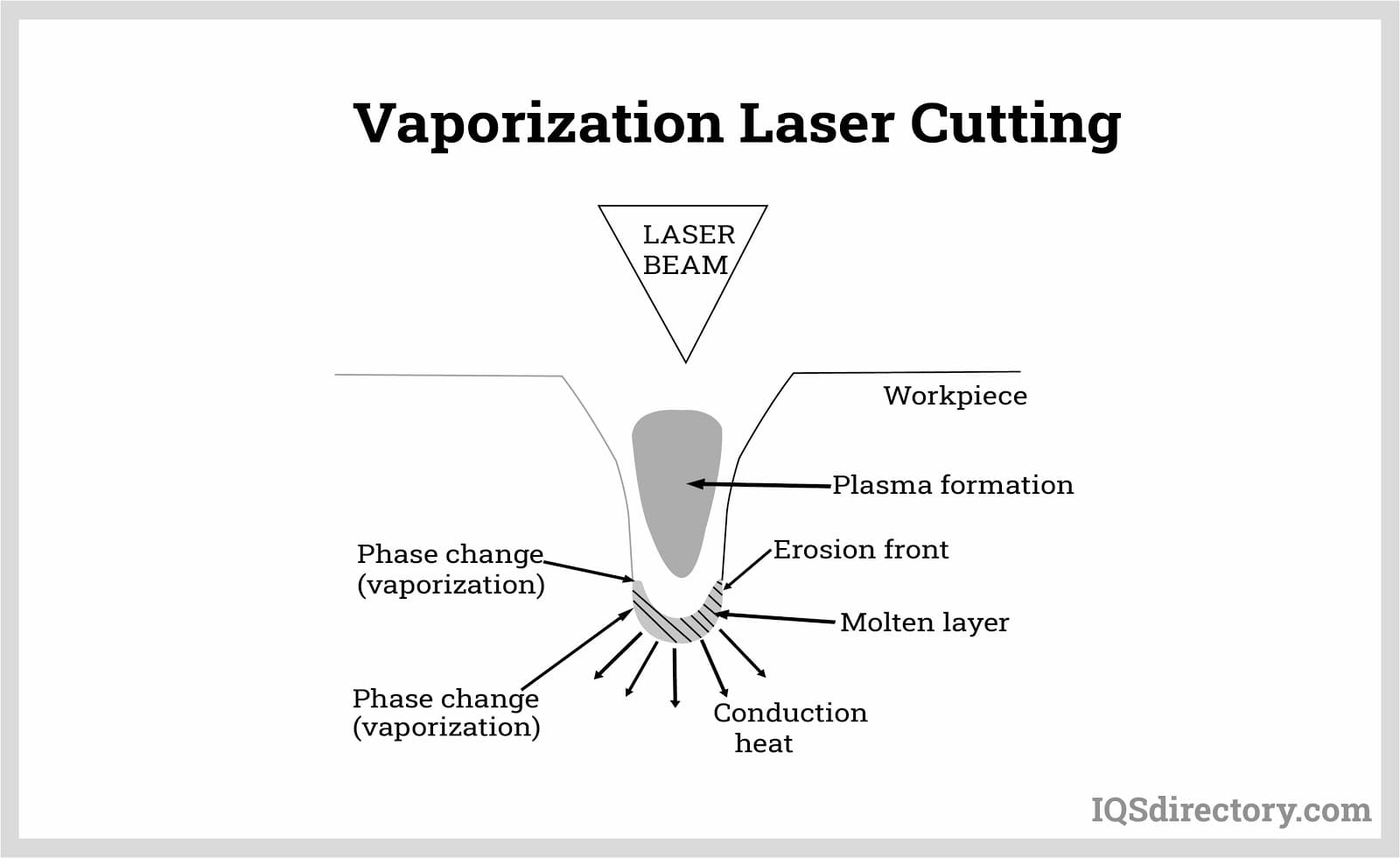
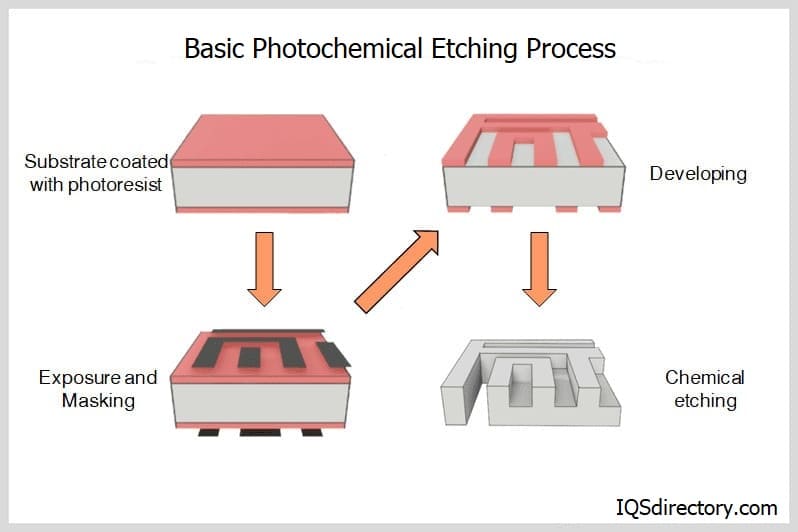
 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services